Shapes¶
Configure¶
Main code
myScreen.setPenSolid(false);
setPenSolid()- prints an empty shape for
falseor a filled shape fortrue.
Use¶
Main code
myScreen.rectangle(16, 16, 47, 31, myColours.black);
myScreen.dRectangle(16, 16, 32, 16, myColours.black);
Most functions accept rectangular coordinates and vector coordinates.
Rectangular coordinates¶
The rectangle coordinates include two points, top-left (16, 16) and bottom-right (37, 31).
point()- displays a point.
line()- draws a line.
rectangle()- draws a rectangle. If
setPenSolid()is set, the rectangle is filled. triangle()- draws a triangle. If
setPenSolid()is set, the triangle is filled. circle()- draws a circle. If
setPenSolid()is set, the circle is filled.
Vector coordinates¶
The rectangle coordinates include one point, top-left (16, 16), and a distance, (32, 16).
dLine()- draws a line.
dRectangle()- draws a rectangle. If
setPenSolid()is set, the rectangle is filled.
Example¶
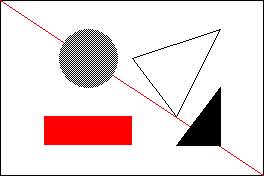
This is the core of the code from example Common_Shapes.ino.

Main code
void displayShapes()
{
myScreen.setOrientation(myOrientation);
uint16_t x, y, dx, dy;
uint16_t z, dz;
x = myScreen.screenSizeX();
y = myScreen.screenSizeY();
dx = x / 6;
dy = y / 6;
z = min(x, y);
dz = min(dx, dy);
myScreen.setPenSolid(false);
myScreen.dRectangle(0, 0, x, y, myColours.black);
myScreen.dLine(0, 0, x, y, myColours.red);
myScreen.triangle(dx * 3, dy * 2, dx * 5, dy, dx * 4, dy * 4,
myColours.black);
myScreen.setPenSolid(true);
myScreen.circle(dx * 2, dy * 2, dz, myColours.grey);
myScreen.dRectangle(dx, dy * 4, dx * 2, dy, myColours.red);
myScreen.triangle(dx * 4, dy * 5, dx * 5, dy * 3, dx * 5, dy * 5,
myColours.black);
myScreen.flush();
}